[작성자:] Jun-Young Paeng(팽준영)
1962년 동아일보가 조명했던 ‘턱얼굴 수술의 마이다스 손’ 민병일 교수
구강악안면외과 전문의 필독 저널- 100 ‘must read’ OMFS articles
구강악안면외과 전문의 필독 저널리스트
대한구강악안면외과학회에서 전공의들을 위해 제시한 추천저널입니다. 교과서는 어느정도 합의된 내용을 다룰 수 밖에 없어 그 뒤에 있는 여러 의견들을 다 기술하지 못한다는 것인데 다양한 인용과 실험적인 부분들을 살펴 볼 수 있다는 점에서 논문 리뷰는 반드시 필요하다고 할 수 있습니다. 모든 논문을 다 읽어서 정리해 낼 수 있으면 좋겠지만, 개념의 발전에 중요한 논문들은 찾아서 읽는 것이 필요하여 전문의로서 읽어야 할 논문은 정리한 것입니다. 다소 오래된 논문도 포함하고 있지만, 그래도 지금의 개념이 생기는데 기본이 되는 것이라 포함이 되어 있습니다. 최신의 논문이 포함되면 좋겠지만, 좀 더 검증이 되는 시간이 필요한데, 그런 논문들은 오히려 ‘올해의 논문” 같은 형식으로 묶여지는 것이 나을 것 같기도 합니다. 좀 묵었지만, 잘 정리되고 모범적인 논문을 선택해야 되지 않을까 생각됩니다. 계속 100개 내외정도로 유지되는 것이 어떨까 생각되고, 그대로 유지해서는 안되며, 3-4년 주기로 반 정도를 교체하는것도 어떨까 생각됩니다. 어쨋든 시간이 갈수록 업데이트는 필수적일 것으로 생각됩니다. 논문의 원문을 pdf로 제공하면 좋겠지만, 저작권등 관련 온라인 상이라는 제한점이 있어서 목록만 올립니다.
혹시 정말 좋은 논문이 있어 필독 논문에 추천할 논문이 있으면 추천 부탁드립니다. 필독 눈문에 대해 삭제, 교체 등 평가를 해주시면 토의하여 반영 하였으면 합니다.
- Farbod F, Kanaan H, Farbod J: Infective endocarditis and antibiotic prophylaxis prior to dental/oral procedures: latest revision to the guidelines by the American Heart Association published April 2007. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38: 626, 2009.
- Aframian DJ, Lalla RV, Peterson DE: Management of dental patients taking common hemostasis-altering medications. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 103 Suppl: S45.e1, 2007.
- Doonquah L, Mitchell AD: Oral Surgery for Patients on Anticoagulant Therapy: Current Thoughts on Patient Management. Dent Clin North Am 56: 25, 2012.
- Turner M, Aziz SR: Management of the pregnant oral and maxillofacial surgery patient. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 60: 1479, 2002.
- Petranker S, Nikoyan L, Ogle OE: Preoperative Evaluation of the Surgical Patient. Dent Clin North Am 56: 163, 2012.
- Paxton K, Thome DE: Efficacy of Articaine Formulations: Quantitative Reviews. Dent Clin North Am 54: 643, 2010.
- CHOI W, SAMMAN N: Risks and benefits of deliberate hypotension in anaesthesia: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 37: 687, 2008.
- Erdogmus S, Govsa F, Celik S: Anatomic position of the lingual nerve in the mandibular third molar region as potential risk factors for nerve palsy. J Craniofac Surg 19: 264, 2008.
- Long H, Zhou Y, Liao L, Pyakurel U, Wang Y, Lai W: Coronectomy vs. total removal for third molar extraction: a systematic review. J Dent Res 91: 659, 2012.
- Halpern LR, Dodson TB: Does prophylactic administration of systemic antibiotics prevent postoperative inflammatory complications after third molar surgery? J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65: 177, 2007.
- Ren Y-F, Malmstrom HS: Effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis in third molar surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65: 1909, 2007.
- Pogrel MA, Dorfman D, Fallah H: The anatomic structure of the inferior alveolar neurovascular bundle in the third molar region. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67: 2452, 2009.
- Donos N, Kostopoulos L, Karring T: Augmentation of the mandible with GTR and onlay cortical bone grafting. An experimental study in the rat. Clin Oral Implants Res 13: 175, 2002.
- Mavrogenis AF, Dimitriou R, Parvizi J, Babis GC: Biology of implant osseointegration. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 9: 61, 2009.
- Solar P, GEYERHOFER U, TRAXLER H, WINDISCH A: Blood supply to the maxillary sinus relevant to sinus floor elevation procedures. Clin Oral Implants Res, 1999.
- Marx RE: Bone and bone graft healing. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 19: 455, 2007.
- Darby I, Chen S, De Poi R: Ridge preservation: what is it and when should it be considered. Australian Dental Journal 53: 11, 2008.
- Renvert S, Polyzois I, Claffey N: Surgical therapy for the control of peri-implantitis. Clin Oral Implants Res 23: 84, 2012.
- Katsumi Y, Tanaka R, Hayashi T, Koga T, Takagi R, Ohshima H: Variation in arterial supply to the floor of the mouth and assessment of relative hemorrhage risk in implant surgery. Clin Oral Implants Res: n, 2011.
- Aghaloo TL, Moy PK: Which hard tissue augmentation techniques are the most successful in furnishing bony support for implant placement? Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 22 Suppl: 49, 2007.
- He D, Yang C, Chen M, Jiang B, Wang B: Intracapsular condylar fracture of the mandible: our classification and open treatment experience. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67: 1672, 2009.
- Haug RH, Serafin BL: Mandibular Angle Fractures: A Clinical and Biomechanical Comparison-the Works of Ellis and Haug. Cranial Maxillofac Trauma Reconstruction 1: 31, 2008.
- Ellis E: Open reduction and internal fixation of combined angle and body/symphysis fractures of the mandible: how much fixation is enough? J Oral Maxillofac Surg 71: 726, 2013.
- Chrcanovic BR: Open versus closed reduction: diacapitular fractures of the mandibular condyle. Oral Maxillofac Surg 16: 257, 2012.
- Kyzas PA, Saeed A, Tabbenor O: The treatment of mandibular condyle fractures: a meta-analysis. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 40: e438, 2012.
- Poort LJ, van Neck JW, van der Wal KGH: Sensory testing of inferior alveolar nerve injuries: a review of methods used in prospective studies. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67: 292, 2009.
- Haspel AC, Coviello VF, Stevens M: Retrospective study of tracheostomy indications and perioperative complications on oral and maxillofacial surgery service. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70: 890, 2012.
- Ellis E: A method to passively align the sagittal ramus osteotomy segments. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65: 2125, 2007.
- Obwegeser HL, Makek MS: Hemimandibular hyperplasia–hemimandibular elongation. J Maxillofac Surg 14: 183, 1986.
- Colella G, Cannavale R, Vicidomini A, Lanza A: Neurosensory disturbance of the inferior alveolar nerve after bilateral sagittal split osteotomy: a systematic review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65: 1707, 2007.
- Gabrielli MFR: Stable fixation of the sagittal split ramus osteotomy. Selective readings of oral and maxillofacial surgery 15: 1, 2012.
- Kramer F-J, Baethge C, Swennen G, Teltzrow T, Schulze A, Berten J, Brachvogel P: Intra- and perioperative complications of the LeFort I osteotomy: a prospective evaluation of 1000 patients. J Craniofac Surg 15: 971, 2004.
- Koudstaal MJ, Wolvius EB, Schulten AJM, Hop WCJ, van der Wal KGH: Stability, tipping and relapse of bone-borne versus tooth-borne surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion; a prospective randomized patient trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38: 308, 2009.
- Hsu SSP, Huang CS, Chen PKT, Ko EWC, Chen YR: The stability of mandibular prognathism corrected by bilateral sagittal split osteotomies: a comparison of bi-cortical osteosynthesis and mono-cortical osteosynthesis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 41: 142, 2012.
- Solano-Hernández B, Antonarakis GS, Scolozzi P, Kiliaridis S: Combined Orthodontic and Orthognathic Surgical Treatment for the Correction of Skeletal Anterior Open-Bite Malocclusion: A Systematic Review on Vertical Stability. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2012.
- Mattos CT, Vilani GNL, Sant’Anna EF, Ruellas ACO, Maia LC: Effects of orthognathic surgery on oropharyngeal airway: a meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 40: 1347, 2011.
- Arnett GW, Bergman RT: Facial keys to orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning–Part II. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 103: 395, 1993.
- Arnett GW, Bergman RT: Facial keys to orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning. Part I. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 103: 299, 1993.
- Sarver DM, Sample LB: How to Avoid Surgical Failures. Seminars in Orthodontics 5: 257, 2012.
- OBWEGESER H: Orthognathic Surgery and a Tale of How Three Procedures Came to Be: A Letter to the Next Generations of Surgeons. Clin Plast Surg 34: 331, 2007.
- Becker OE, Avelar RL, Göelzer JG, Dolzan ADN, Haas Júnior OL, De Oliveira RB: Pharyngeal Airway Changes in Class III Patients Treated With Double Jaw Orthognathic Surgery-Maxillary Advancement and Mandibular Setback. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70: e639, 2012.
- Steel BJ, Cope MR: Unusual and rare complications of orthognathic surgery: a literature review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70: 1678, 2012.
- Stal S, Brown RH, Higuera S, Hollier LH, Byrd HS, Cutting CB, Mulliken JB: Fifty years of the Millard rotation-advancement: looking back and moving forward. Plast Reconstr Surg 123: 1364, 2009.
- Tajima S, Maruyama M: Reverse-U incision for secondary repair of cleft lip nose. Plast Reconstr Surg 60: 256, 1977.
- Yuzuriha S, Oh AK, Mulliken JB: Asymmetrical bilateral cleft lip: complete or incomplete and contralateral lesser defect (minor-form, microform, or mini-microform). Plast Reconstr Surg 122: 1494, 2008.
- Yuzuriha S, Mulliken JB: Minor-form, microform, and mini-microform cleft lip: anatomical features, operative techniques, and revisions. Plast Reconstr Surg 122: 1485, 2008.
- Mulliken JB: Primary repair of bilateral cleft lip and nasal deformity. Plast Reconstr Surg 108: 181, 2001.
- Mulliken JB, Martínez-Pérez D: The principle of rotation advancement for repair of unilateral complete cleft lip and nasal deformity: technical variations and analysis of results. Plast Reconstr Surg 104: 1247, 1999.
- Cheung LK, Chua HDP: A meta-analysis of cleft maxillary osteotomy and distraction osteogenesis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35: 14, 2006.
- Sommerfeldt DW, Rubin CT: Biology of bone and how it orchestrates the form and function of the skeleton. European spine journal : official publication of the European Spine Society, the European Spinal Deformity Society, and the European Section of the Cervical Spine Research Society 10 Suppl 2: S86, 2001.
- Bagheri SC, Khan HA, Cuzalina A: Rhinoplasty: current therapy. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 24: ix, 2012.
- Niamtu J: Cosmetic blepharoplasty. Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 12: 91, 2004.
- Reyneke JP, Ferretti C: Clinical Assessment of the Face. Seminars in Orthodontics 18: 172, 2012.
- Vigliante CE: Anatomy and Functions of the Muscles of Facial Expression. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 17: 1, 2005.
- Eppley BL, Dadvand B: Injectable soft-tissue fillers: clinical overview. Plast Reconstr Surg 118: 98e, 2006.
- Beer K, Beer J: Overview of facial aging. Facial Plast Surg 25: 281, 2009.
- Niamtu J: Complications in fillers and Botox. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 21: 13, 2009.
- Fattahi T, Bolding SL, Griffin JE, Owsley TG: Cosmetic maxillofacial surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70: e310, 2012.
- Green J, Weiss A, Stern A: Lasers and radiofrequency devices in dentistry. Dent Clin North Am 55: 585, 2011.
- Jaspers GWC, Pijpe J, Jansma J: The use of botulinum toxin type A in cosmetic facial procedures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 40: 127, 2011.
- Mercuri LG: Re: Dimitroulis, G: The role of surgery in the management of disorders of the temporomandibular joint: a critical review of the literature. Part I. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2005;34:107-13. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34: 703, 2005.
- Re: Dimitroulis, G. The role of surgery in the management of disorders of the temporomandibular joint: a critical review of the literature. Part 2. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2005: 34: 231-237. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35: 284, 2006.
- Dolwick MF: Temporomandibular joint surgery for internal derangement. Dent Clin North Am 51: 195, 2007.
- Dimitroulis G: The role of surgery in the management of disorders of the Temporomandibular Joint: a critical review of the literature. Part 1. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34: 107, 2005.
- Dimitroulis G: The role of surgery in the management of disorders of the temporomandibular joint: a critical review of the literature. Part 2. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34: 231, 2005.
- Schendel SA, Tulasne J-F, Linck DW: Idiopathic condylar resorption and micrognathia: the case for distraction osteogenesis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65: 1610, 2007.
- Posnick JC, Fantuzzo JJ: Idiopathic condylar resorption: current clinical perspectives. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65: 1617, 2007.
- Dimitroulis G: Temporomandibular joint surgery: what does it mean to the dental practitioner? 56: 257, 2011.
- Al-Kayat A, Bramley P: A modified pre-auricular approach to the temporomandibular joint and malar arch. Br J Oral Surg 17: 91, 1979.
- Roberts WE, Huja S, Roberts JA: Bone modeling: biomechanics, molecular mechanisms, and clinical perspectives. Seminars in Orthodontics 10: 123, 2004.
- Mercuri LG: A rationale for total alloplastic temporomandibular joint reconstruction in the management of idiopathic/progressive condylar resorption. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65: 1600, 2007.
- Mercuri LG, Edibam NR, Giobbie-Hurder A: Fourteen-year follow-up of a patient-fitted total temporomandibular joint reconstruction system. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65: 1140, 2007.
- Historical development of alloplastic temporomandibular joint replacement after 1945 and state of the art. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38: 909, 2009.
- Mercuri LG: The use of alloplastic prostheses for temporomandibular joint reconstruction. YJOMS 58: 70, 2000.
- Westermark A: Total reconstruction of the temporomandibular joint. Up to 8 years of follow-up of patients treated with Biomet(®) total joint prostheses. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 39: 951, 2010.
- Giannakopoulos HE, Sinn DP, Quinn PD: Biomet Microfixation Temporomandibular Joint Replacement System: a 3-year follow-up study of patients treated during 1995 to 2005. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70: 787, 2012.
- Toda K: Operative treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: review of current techniques. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 106: 788, 2008.
- Prasad S, Galetta S: Trigeminal neuralgia: historical notes and current concepts. The neurologist 15: 87, 2009.
- Ord R, Coletti D: Cervico-facial necrotizing fasciitis. Oral Dis 15: 133, 2009.
- Pitak-Arnnop P, Sader R, Dhanuthai K, Masaratana P, Bertolus C, Chaine A, Bertrand J, Hemprich A: Management of osteoradionecrosis of the jaws: An analysis of evidence. Eur J Surg Oncol 34: 1123, 2008.
- Brannon RB, Fowler CB: Benign fibro-osseous lesions: a review of current concepts. Adv Anat Pathol 8: 126, 2001.
- Madras J, Lapointe H: Keratocystic odontogenic tumour: reclassification of the odontogenic keratocyst from cyst to tumour. J Can Dent Assoc 74: 165, 2008.
- Gomes CC, Duarte AP, Diniz MG, Gomez RS: Review article: Current concepts of ameloblastoma pathogenesis. J Oral Pathol Med 39: 585, 2010.
- Brown JS, Rogers SN, McNally DN, Boyle M: A modified classification for the maxillectomy defect. Head Neck 22: 17, 2000.
- Xu G-Z, Zhu X-D, Li M-Y: Accuracy of whole-body PET and PET-CT in initial M staging of head and neck cancer: A meta-analysis. Head Neck 33: 87, 2011.
- Izumo T: Oral premalignant lesions: from the pathological viewpoint. International journal of clinical oncology / Japan Society of Clinical Oncology, 2011.
- Wong WL, Batty V: Role of PET/CT in maxillo-facial surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 47: 259, 2009.
- Robbins KT, Ferlito A, Shah JP, Hamoir M, Takes RP, Strojan P, Khafif A, Silver CE, Rinaldo A, Medina JE: The evolving role of selective neck dissection for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270: 1195, 2013.
- Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJM, Brakenhoff RH: The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 11: 9, 2010.
- Shah JP, Candela FC, Poddar AK: The patterns of cervical lymph node metastases from squamous carcinoma of the oral cavity. Cancer 66: 109, 1990.
- Keefe DM, Schubert MM, Elting LS, Sonis ST, Epstein JB, Raber-Durlacher JE, Migliorati CA, McGuire DB, Hutchins RD, Peterson DE, Cancer FTMSSOTMAOSCI, Oncology ATISFO: Updated clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of mucositis. Cancer 109: 820, 2007.
- Shekar K, Singh M, Godden D, Puxeddu R, Brennan PA: Recent advances in the management of salivary gland disease. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 47: 594, 2009.
- POGREL MA, Podlesh S, Anthony JP, Alexander J: A comparison of vascularized and nonvascularized bone grafts for reconstruction of mandibular continuity defects. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55: 1200, 1997.
- Langstein HN, Robb GL: Lip and perioral reconstruction. Clin Plast Surg 32: 431, 2005.
- Robey AB, Spann ML, McAuliff TM, Meza JL, Hollins RR, Johnson PJ: Comparison of miniplates and reconstruction plates in fibular flap reconstruction of the mandible. Plast Reconstr Surg 122: 1733, 2008.
- Pohlenz P, Klatt J, Schön G, Blessmann M, Li L: Microvascular free flaps in head and neck surgery: complications and outcome of 1000 flaps. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 41: 739, 2012.
- Thoma A, Levis C, Young JEM: Oromandibular reconstruction after cancer resection. Clin Plast Surg 32: 361, 2005.
- Dalgorf D, Higgins K: Reconstruction of the midface and maxilla. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 16: 303, 2008.
- Novakovic D, Patel RS, Goldstein DP, Gullane PJ: Salvage of failed free flaps used in head and neck reconstruction. Head Neck Oncol 1: 33, 2009.
- Toshihiro Y, Nariai Y, Takamura Y, Yoshimura H, Tobita T, Yoshino A, Tatsumi H, Tsunematsu K, Ohba S, Kondo S, Yanai C, Ishibashi H, Sekine J: Applicability of buccal fat pad grafting for oral reconstruction. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 42: 604, 2013.
- Yousuf S, Tubbs RS, Wartmann CT, Kapos T, Cohen-Gadol AA, Loukas M: A review of the gross anatomy, functions, pathology, and clinical uses of the buccal fat pad. Surg Radiol Anat 32: 427, 2010.
- Pitak-Arnnop P, Hemprich A, Pausch NC: Evidence-based oral and maxillofacial surgery: some pitfalls and limitations. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69: 252, 2011.
- Mommaerts MY, Foster ME, Gundlach KKH: How to do clinical research in cranio-maxillo-facial surgery. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 40: 97, 2012.
- Archibald DJ, Carlson ML, Friedman O: Pitfalls of Nonstandardized Photography. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 18: 253, 2010.
- Sprague S, McKay P, Thoma A: Study Design and Hierarchy of Evidence for Surgical Decision Making. Clin Plast Surg 35: 195, 2008.
- Aziz SR: The person behind the name. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55: 847, 1997.
- Aziz SR: The person behind the name: part 2. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61: 1212, 2003.
구강암 안내
구강암이란…
구강암은 주로 입안과 위, 아래턱과 그 주변부에 발생하는 암으로 입안의 점막에서 발생하는 편평세포암이 가장 흔합니다. 이외에 침샘에서 발생하는 침샘암, 육종등이 발생할 수 있습니다. 입안에 생기는 부위에 따라 혀에 생기는 경우 설암, 잇몸에 생기는 경우 치은암 등으로 불리기도 합니다.
보통 50-60대에 가장 많이 발생하는 것으로 알려져 있습니다.
구강암의 정확한 원인은 알려져 있지 않습니다. 일반적으로 구강암의 위험요인으로는 흡연, 음주, 바이러스, 방사선, 자외선, 식습관, 영야결핍, 유전적 감수성등이 거로되고 있습니다.
| 구강암의 일반적 증상 |
구강암은 다른 부위의 암과는 달리 대부분 육안으로 판별이 가능합니다. 따라서 병원에 구강암 검진을 위하여 정기적으로 내원하면 조기진단이 비교적 쉽습니다. 구강암을 가진 환자들의 주된 증상 중의 하나는 구강내의 병변으로 쑤시는 듯한 통증 때문에 병원을 찾는 경우가 많습니다. 그러나 초기 암의 경우는 통증이 없는 경우가 더 많기 때문에 통증의 유무가 구강암의 증상과는 반드시 연관선이 있는 것은 아닙니다.
- 입안이 헐었다.
혀나 볼점막, 입천장, 입술 등에 발생하는 궤양은 구내염 같은 염증성 병변이 가장 많아 1-2주 정도면 통증도 사라지고 궤양도 없어지지만, 3주 정도 지나도 없어지지 않는 궤양은 단순한 염증으로 보기 어렵기 때문에 조직검사를 받아보는 것이 좋습니다.
- 입안에 하얀 또는 붉은 병변이 있다.
구강내 점막에 지워지지 않는 백색 병소가 있는 것을 백반증이라고 하는데, 이러한 백반증이나 붉은 홍반증 등은 구강암으로 진행될 수 있는 병소로 필요한 경우 조직검사를 시행하여 정확한 감별을 시행하여야 합니다.
- 혀나 입안이 아프다.
통증은 초기암에 비해 진행암에서 많고 암조직에 염증이 심하면 2차적으로 통증을 유발할 수 있습니다. 하지만 입안에 생기는 많은 다른 질환들이 통증을 유발하기 때문에 감별이 필요합니다.
- 입안에 혹이 만져진다.
입안의 혹은 부위에 따라 암일 수도 있고 아닐 수도 있기 때문에 전문가의 진단이 필요합니다.
- 이가 갑자기 흔들리거나, 이를 뽑은 후 상처가 아물지 않는다.
잇몸질환(풍치)이 있을 경우 이가 흔들리지만, 전혀 증상이 없는 치아가 갑자기 흔들리면 암에 의해 잇몸이 갑자기 손상된 것일 수 있습니다. 또한 이를 뽑은 자리가 한달이상 아물지 않는 경우 검사가 필요합니다.
- 목에 혹이 만져진다.
구강암이 진행되면 주로 턱 아래의 림프절로 암이 전이되는데 이러한 경우 목에 혹이 만져지기도 합니다.
설암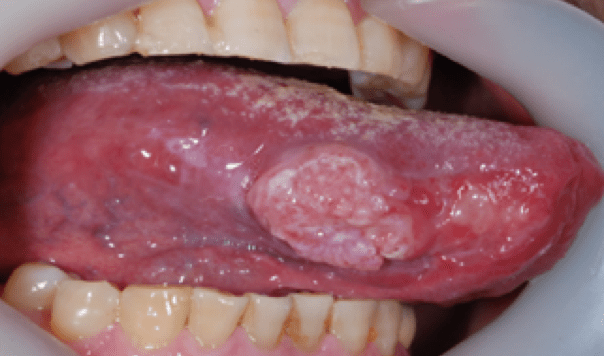 |
치은암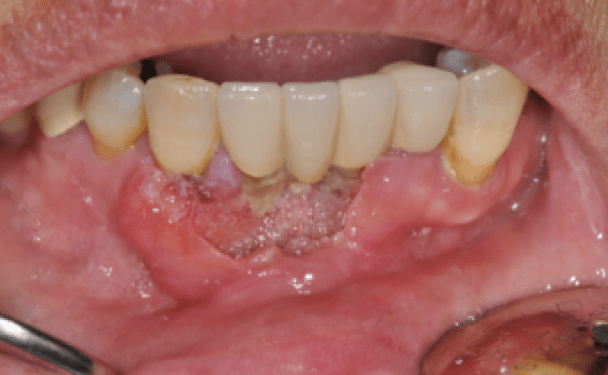 |
구개암(입천정) |
구강저암(혀아래) |
| 구강암의 검사방법 |
구강암의 진단과 병기의 판정을 위해서는 아애의 검사들을 시행하게 됩니다. 조직검사에서 구강암으로 진단이 되면 구강암의 크기, 목 림프절 전이, 전신적 전이를 여부등을 검사하게 됩니다.
- 조직검사
- 방사선사진 검사
- 전산화 단층촬영 (CT 촬영)
- 자기공명영상(MRI)
- 핵의학 검사(뼈스켄)
- 목 초음파 검사
- 양전자방출 단층촬영(PET/CT)
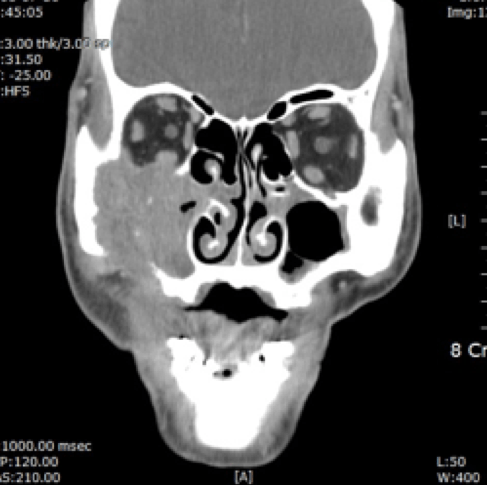 전산화단층촬영 전산화단층촬영 |
 양전자방출 단층촬영 양전자방출 단층촬영 |
| 구강암의 병기 |
구강암의 진행단계를 나타내는 병기는 원발암의 크기나 목의 림프절 전이, 원격전이 여부에 따라 1,2,3,4기로 병기를 나누게 됩니다. 병기가 높아질수록 구강암이 진행된 정도를 나타냅니다.
| 구강암의 치료 |
구강암은 다른 암과 마찬가지로 초기에 발견될수록 기능장애도 최소로 하면서 완치의 가능성도 있습니다. 구강암 치료의 일차적인 목적은 암을 제거하고 재발률을 낮추는 것입니다. 또한 이와 함께 구강내 기능과 얼굴의 외형도 최소로 하고 음식을 먹고, 삼키고, 말하는 기능 등을 보존하도록 노력하고 있습니다.
구강암 치료방법을 결정하는 것은 병기, 연령, 전신상태, 결손부위 등을 고려하여 결정하게 됩니다. 수술이 가능한 경우 수술적 치료를 우선하게 됩니다. 진행된 암의 경우는 수술과 방사선 치료를 병용하여 치료하는 것이 완치율을 높일 수 있는 방법입니다. 약물을 사용하는 항암화학용법은 현재까지 구강암의 일차적인 치료방법으로 사용하지는 않으며, 부가적인 치료방법으로 사용되고 있습니다.
- 구강암의 수술
- 방사선 치료
- 항암화학요법
| 전완피판을 이용한 재건술
|
 |
| 구강암의 수술적 치료 |
구강암의 수술은 구강내의 암부위를 절제하고 필요한 경우 목의 림프절을 예방 혹은 치료적 목적으로 제거하거나, 구강의 재건술을 시행하여 말하고 먹고 씹는 기능 및 외관을 원래대로 유지하도록 시행됩니다.
- 암의 절제술
- 목의 림프절 절제술(경부청소술)
- 재건술
초기암의 경우 재건술이 필요하지 않지만, 광범위 절제술을 시행한 경우는 구강내 결손부의 일차 봉밥이 어려우므로 제거된 구강연조직을 대신하는 피부조직을 이식해야 합니다. 재건술에는 팔의 피부를 채취하는 유리전완피판술을 가장 많이 사용합니다.
또한 턱뼈가 연조직과 함께 절제된 경우는 주로 다리의 비골뼈와 피부를 이식하여 얼굴의 외형을 유지하기도 합니다.
입천장을 포함한 위턱뼈을 제거한 후에는 이식 수술보다는 특수틀니를 제작하여 기능을 회복하는 것이 보편적입니다.
| 방사선 치료 |
방사선치료는 수술과 함께 가장 많이 사용되는 치료방법입니다. 방사선 치료는 수술을 먼저 시행한 경우수술 후 4-6주정도 상처가 어느정도 치유된 후 시작하게 됩니다. 치료료기간은 1주일에 5회, 매일 방사선 조사를 하여 6-7주 정도 시행합니다.
| 구강암의 재발 및 전이 |
구강암의 병기가 진행될수록 재발의 가능성이 커지게 됩니다. 모든 사람이 재발하는 것은 아니지만, 일단 재발이 되면 대부분 수술 후 2년 내에 발생하게 됩니다. 이후에도 재발의 가능성은 있지만 시간이 흐르면서 가능성은 감소하기 때문에 보통 5년 정도 재발이 없었다면 일반적으로 암이 완치되었다고 생각합니다. 전이가 발생하는 경우가 있으며, 가장 흔한 부위는 폐이며, 그 다음으로는 간, 뼈 등이나 다른 모든 신체부뷔로도 전이가 될 수 있습니다.
재발암의 경우에도 조기에 발견하면 치료의 가능성이 높아져 정기적으로 내원하는 것이 가장 중요합니다. 환자의 상태에 따라 내원 주기가 다르지만 일반적으로 다음과 같이 권장하고 있습니다.
- 수술 후 첫 1년 : 1-3개월 마다
- 수술 후 2년째 : 2-4개월 마다
- 수술 후 3-5년째 : 4-6개월 마다
- 수술 후 5년 이후 : 6-12개월 마다
구강암 증례 토론회
일시 : 2016년 6월 18일 (토) 14:00 –
장소 : 전북대학교 치과병원 지하 1층 강당
김묵규 부산대학교 병원장님이 구강암 연구소장으로 취임하시고 처음 열리는 구강암 증례 토론회였다. 참석자가 많지는 않았으나, 활발한 토론이 이루어졌다.


20회 대한구순구개열학회 학술대회
Korean Association of Cleft lip and Palate
일시 : 2016년 6월 11일
장소 : 서울대학교 치과병원 지하1층 제1강의실
주제 : Ideal team approach in cleft patients

Fig. 1. 연자초청 식사 2016.06.10 용수산비원. Kamioka 교수님, Mori 교수님, 박용종 선생님

Fig. 2 Kamioka 교수님의 강의. Kamioka 교수님은 교정과 교수님으로 Okayama 대학의 cleft center의 director를 맡아서 운영하고 계신다.

Fig. 3 Mori 교수님의 강의

Fig. 4. 전북대 신효근 교수님의 정년을 앞두고 기념 강연이 있으셨다. 이번에 구순구개열 환자의 치료경험을 담아내신 책을 발간하고, 학회기간의 수익금을 학회에 기부해 주셨다.
베트남 구순구개열 수술 봉사활동
- 일시 : 2016.5.15 – 21
- 장소 : 베트남 호치민시 호시민 구강악안면병원(시립) (HCM Odonto-Maxillo-Facial Hospital)
- 참가자
- 박영욱 (강릉원주대학교 구강악안면외과)
- 김성곤 (강릉원주대학교 구강악안면외과)
- 팽준영 (경북대학교 구강악안면외과)
- 황대석 (부산대학교 구강악안면외과)
- 김주원 (한림대하교 평촌성심병원 구강악안면외과)
- 김철준 (서울의료봉사재단 재무이사)
- 우인희 (한림대하교 평촌성심병원 구강악안면외과)
- 박동철 (부산대학교병원 구강악안면외과)
- 수술 (총 28례)
- cleft lip (6명), cleft palate (14명), 2ndary correction (8명)
- 주요일정
- 5.15 : 인천공항 출발
- 5.16 : 예진
- 5.17-20 : 수술
- 5.21 : 귀국

Fig. 1. 출발전 인천공항

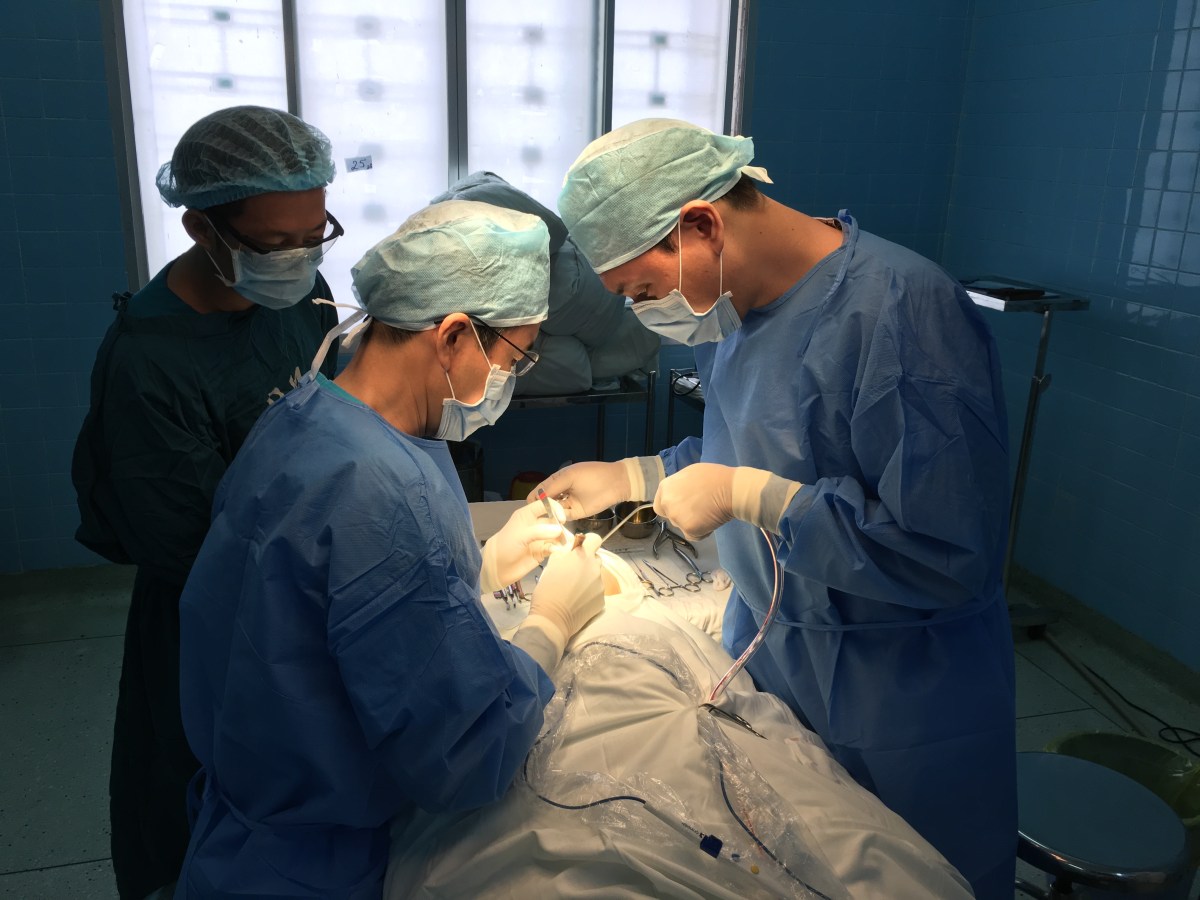
Fig. 2 호치민시 구강악안면병원
Fig. 3 수술 준비 구강악안면외과 병원에서 근무하는 scrub nurse. 베트남에서 수술하면 항상 느끼게 되는 것은 말은 잘 통하지 않는데 수술을 하는 데 별 어려움없이 도와준다는 것이다. 수술의 과정을 모두 이해하고 있으며, 다음 술식까지 다 알고, 수술까지도 도와주는 것으로 봐서는 수술실 간호사는 세계 어디를 가나 전문가적인 스킬을 가지고 있다는 생각이 든다.
Fig. 4 단장님인 박영욱 교수님 수술하시는 모습
Fig. 5. 마침 호치민시에서 마취과 선생님들이 모여 미국에서 온 마취과 의사분의 지도로 소아구강악안면외과 환자에서의 마취에 대해 교육중에 있다.
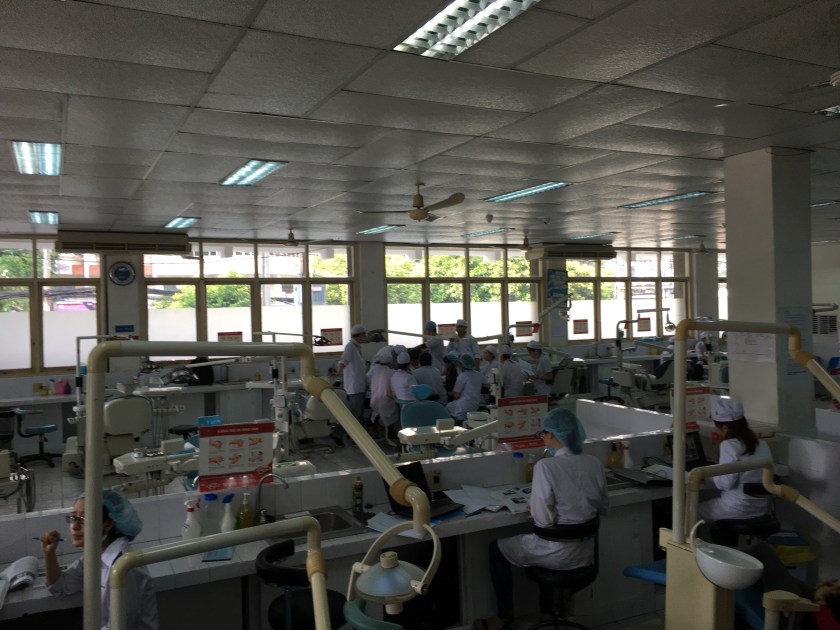

Fig. 6 방문했던 호치민 의약학대학의 구강의학원병원. 학생들의 실습위주로 병원이 운영되고 있는 교육병원이다.
Winter meeting of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery in Tohoku
일시 : 2016. 2.25-27
장소 : Zao Onsen (Zao Mountain), Tohoku, Japan
참가자 : 일본의 젊은 구강외과의사들, Peter Kessler (Netherland), Tetsu Takahashi
3일간의 세미나를 통해 일본의 젊은 구강악안면외과의사들의 activity를 확인할 수 있었다. 깊이 파는 것은 일본의 특징이 아니라 모든 학문하는 의사들이 가져야할 기본적인 자세이다. 열심히 하는 모습에 많은 자극을 받을 수 있었다. 또한 이런 모임이 하나의 문화를 만들고 의미있고 낭만적인 일이 될 수 있도록 노력하는 점도 배워야할 부분으로 생각된다.

Fig. 1. Yamuchi의 orientation 설명

Fig. 2 Takahashi 교수님의 개회사

Fig. 3. Zao 산으로 가는 길은 2월 말인데도 눈으로 덮혀 있다. 설국으로 가는 관문

FIg. 4 Kessler 교수의 축사

Fig. 5 제1회 동기구강외과임상연구회

Fig. 6 마을은 눈으로 덮혀있다. 눈이 소음을 흡수하여 소리가 사라진 듯한 느낌을 주는 곳이다.

Fig. 7 마을 어디나 김이 솟아 오른다.

Fig. 8 아침 식사는 스키장을 바라보며

Fig. 9 아침에는 열심히 세미나를 한다.

Fig. 10 식사중

Fig. 11 Zao온천은 유황온천으로 유명하다. 냄새와 함께 계속 마을 곳곳에서 흘러나온다. 그냥 온천만 즐기면 몇천원 하지 않는 많은 온천들이 마을에 널려있다.
일본턱관절학회 – 나고야
구강암의 조기 검진
[건강칼럼] 간단하고 저렴한 구강암 조기검진
 |
치통도 참기 어려운 통증 중 하나이지만, 입 안의 점막(혀, 입술, 볼, 입천장 등)은 음식을 먹다가 혀를 깨물거나, 뜨겁고 날카로운 음식 등 외부 자극으로 크고 작은 상처가 잘 생긴다. 이곳이 헐면 그 고통은 말로 표현하기 힘들 정도다. 다행히 1~2주 지나면 저절로 낫지만 나을 때까지 참는 것도 고역이다.
이렇듯 구강은 우리가 매일 말하고, 식사하고, 숨쉬는 친숙한 곳이지만 불편함이 느껴지지 않으면 입 안을 자주 들여다 보지 않게 된다. 우리나라는 세계에서도 유래 없이 고가의 건강검진을 많이 하는 나라다. 덕분에 질병 조기 발견은 국민 건강의 향상에 많은 도움을 준다.
구강암은 다른 암에 비해 발생률이 높지 않다. 하지만 다른 암처럼 진행된 구강암의 경우 치료를 하더라도 씹는 기능 감소, 얼굴 추형 등의 후유증이 남을 수 있다. 생명을 위협하는 전이의 가능성이 높아 조기 발견이 예후의 향상에 가장 중요한 요소 중 하나다. 다행히 구강암은 많은 비용을 들이지 않고도 간단히 육안으로 감별할 수 있는 장점이 있다.
위암이나 대장암의 검진도 눈으로 먼저 관찰하고 의심스러운 질환을 떼어내어 검사하지만, 사람 속을 들여다 볼 수 없어 내시경을 이용한다. 입 안은 이런 장비 없이도 잘 들여다 볼 수 있다. 거울로 혹은 치과 검진 시 보는 것만으로도 쉽게 검진할 수 있다.
치과 전문의의 입장에서 구강암도 유방암처럼 자가 검진의 교육과 홍보가 잘 되었으면 하는 바람이다.
그렇다면 구강암 자가검진은 어떻게 할까. 구강암의 경우 ‘2주 이상 상처가 낫지 않을 경우’ ‘갑자기 이유 없이 치아 주변이 붓고 이가 흔들릴 경우’ ‘입 안에서 점점 커지는 혹 같은 것이 있을 경우’ 치과병원을 찾아가야 한다.
만약 의심스러운 병소가 있을 경우 병원에서는 조직검사를 통해 확진하게 된다. 초기의 구강암은 다른 암처럼 전혀 통증이 없을 수 있어, 대수롭지 않게 생각하는 경우가 많다.
일차적인 자가 검진외에도 많은 사람들이 입안의 치료를 받고 있는 치과의원에서 치료 도중에 구강내의 점막도 같이 검진하면 매우 효율적인 조기 검진 방법이 된다. 이를 위해서는 국민과 치과의사들의 관심도 필요하다.
고가의 검진이 필요없는 구강암 조기 검진이 활성화되려면 어떻게 하는 것이 좋을까.
우리는 이미 이러한 운동이 관심과 홍보만으로는 효과적이지 않다는 것을 잘 알고 있다. 국민 건강검진이 자리를 잡았듯이 제도적인 뒷받침도 필요하다. 현재의 건강검진 시스템 내에 자리 잡을 수 있다면, 구강암 검진은 큰 사회적 비용없이도 쉽게 이루어질 수 있을 것이라고 생각된다. 물론 구강암 검진이 구강암의 발생률을 줄이거나 하지는 않겠지만, 적어도 많이 진행되어 병원을 찾는 환자의 비율을 줄일 수 있고, 이로 인해 구강암의 치료 결과가 높아질 수 있다면 의미있는 일이라고 생각된다.
팽준영<경북대치과병원 구강악안면외과 교수>
2014. 10. 14 영남일보 건강 칼럼